Sole Proprietorship Taxation is one of the least understood topics amongst small business owners. If you run a sole proprietorship and have not understood the taxation aspects that affect you and your business, then you might find this article very useful.
The sole proprietors are the backbone of the Indian economy. It would be appropriate to say that the taxes paid by the millions of sole proprietors run our country today. Yet, many sole proprietors do not know about income tax and why filing their income tax return is so beneficial for their business. In this article, we try to cover the income tax aspects that are important for a sole proprietor. If you are running your business as a sole proprietor, please do read the full article.

What is Income Tax?
Income Tax is a direct tax levied by Government of India on earnings of it’s citizen.
Now earning not only mean salary income only. It also include income earned by way of business or profession or any kind of income generated though investments.
Income tax is levied by Government on salaried class, self employed class, corporate class and other class earning income though investments also. In short, every person who is earning some source of income rather who is earning money is required to pay tax to government on his earnings with respect to some rules formed by government.
Income tax being a Direct Tax in nature is non transferable and person earning income himself needs to pay this tax.
Who is liable to file Income Tax Return?
Every individual whose gross total income exceeds the basic exemption limit prescribed by the government is required to file Income Tax Return (ITR).
Now gross total income means the amount arrived at after combining all income earned by person though all heads of income which include salary, house rent, business, interest income, capital gain on sale of shares./ mutual funds or any other asset like house, land etc.
There are many other conditions also in which one need to file ITR. Details of the same are explained in our article “Need to File ITR”.
When is filing of the Income Tax Return mandatory?
- Total income exceeds basic exemption limit (based on age)
- Amount spent on foreign travel in excess of Rs. 2 lakhs
- Payment of electricity bill in excess of Rs. 1 lakh
- Aggregate deposit in bank accounts considering all banks is in excess of Rs. 1 crore
- Any person having income from foreign country
- Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) is more than Rs. 25000/- even though income is below basic exemption limit
- Person who wants to claim Income Tax refund on taxes already paid or deducted by any person
- Who want to carry forward losses to next year
What is FY and AY in Income Tax Return?
FY stands for Financial Year and AY stands for Assessment Year. Let’s understand this with an example.
FY2021-22 means Financial Year 2021-22. This refers to the period from April 2021 to March 2022.
AY 2021-22 means Assessment Year 2021-22. This refers to the period from April 2022 to March 2023.
Income Tax slab for FY 2022-23 (AY 2023-24)
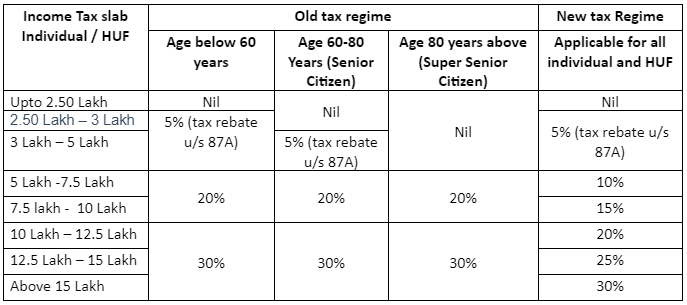
Based on this slab rate every individual / sole proprietorship earning income need to calculate tax as per above slab rate and file their income tax return.
For detailed information about old and new tax regime please read our article “Tax planning tools for sole proprietor”
Sole Proprietorship Tax Obligations
Sole proprietorship is the most common form of running a business in India. Sole proprietor means an individual running business in his own capacity. The individual running the business is called the Sole Proprietor and the business is called the Sole Proprietorship.
Now, the individual has the option to either run the business in his / her own name or he / she can give some name to his business and register this business as a legal entity.
A sole proprietor is also a tax-payer and needs to file the income tax returns for his business. The good thing is that the sole proprietor need not file his personal income tax return separately and business income tax return separately. But the only difference is sole proprietor is not required to file separate tax return for business and he only include income from business in his personal income tax return and file consolidate return. Income tax rate for sole proprietor is similar as it applicable to individual.
Sole Proprietorship Taxation & Individual Income Tax Return - are they different?
Sole proprietor is an individual running business in his personal single capacity, there is only one entity to file ITR i.e. individual. Thus, Individual and sole proprietor is same under income tax and not considered as two different entities.
Sole proprietor with some business name can open bank account with business name and take registration under MSME and GST under business name. But for income tax purpose, both are same and only single return is filed with individual name.
Sole Proprietorship Taxation: Requirements for filing Income Tax Return for a Sole Proprietorship
Permanent Account Number (PAN) is mandatory for all taxpayers. For sole proprietor, a separate PAN is not required and one can file return using their individual PAN only.
Bank account and other registrations under business name will be considered as if it belongs to individual name and accordingly clubbed in income of individual.
Whatever profit individual is earning from business will be added to personal income and then ITR will be filed for individual.
Now to arrive at profit, one should consider all expenses incurred for business and allowed under income tax. Details for this are already explained in our article “Tax planning tools for sole proprietor”
Sole Proprietorship Taxation: Income Tax Return filing forms that every Sole Proprietor needs to know
As per Income Tax, a sole proprietor is required to file
- ITR-4 form where books of accounts are not maintained and presumptive taxation is availed and
- ITR-3 form where books of accounts are maintained.
Presumptive taxation means paying tax at some predetermined profit % based on nature of business.
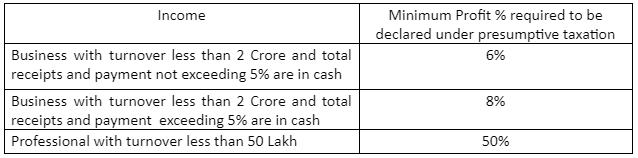
If one want to opt for presumptive taxation, then minimum profit % is required to be shown while filing Income Tax Return. Else audit is required.
Books of Accounts and Audit
Every person being Individual and HUF running business is required to maintain books of accounts if
- Income exceeds Rs. 250000/-
- Total sales/ turnover/ gross receipts are in excess of Rs. 25,00,000/- in any of the 3 previous years
Penalty will be levied by department upto Rs. 25000/- for non-compliance for maintaining books of accounts if you are liable to maintain.
In case your business have a turnover in excess of Rs. 1 Crore during the financial year , then you need to get your books audited with Chartered accountant and submit audit report signed by CA along with IT return.
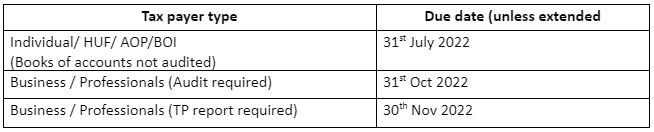
Due dates for filing Income Tax Return in 2022
How to file Income Tax Return of Sole Proprietorship?
Electronic filing or E-filing of Income Tax Return is mandatory by Income Tax department now a days. Earlier one need to go to Income Tax department and need to submit hard copy of form in the department. But now electronic filing means you need to file return online via IT portal
E-filing is beneficial as
- Errors will be reduced as it is already pre-verified by the system
- It will save time and money of both taxpayer and government authority
- It is flexible in time and can be filed from anywhere at any time
- You will get guaranteed confirmation of filing return and it will act as legal proof
Steps to file Income Tax Return of Sole Proprietor
- PAN
- First step is to obtain PAN of individual
- IT portal logn
- Register on Income Tax portal with PAN and login
- Income Tax Return
- From E-filing menu choose Income Tax Return, AY, Form Type
- File all required details in the form and choose upload
- After uploading return e-verify it within 120 days or send signed hard copy
Tax Saving tools for Sole Proprietorship
There are many income tax deductions and allowances allowed while calculating income of sole proprietor and one can take full benefit of these deductions allowed by Income Tax department.
Detailed for this are already explained in our article “Tax saving tools for sole proprietor”.
Some of basic things to keep in mind to minimize tax liability
- Maintain proper books of accounts
- Record all expenses incurred for business which are in cash as well
- Keep track of your investments like LIC, FD, RD and many more
- Depreciation works as major tool for tax saving
- Update oneself from time to time about recent changes
- Don’t forget to consider housing loan if any while calculating your taxable income
- Encourage digital transactions as opposed to cash expenses
- Work out proper business strategy with your tax expert to minimize tax and maximize profit
Benefits of filing Income Tax Return for Sole Proprietorship
Use as address proof
One can use ITR processing order as proof of address
Use as Income proof
ITR filed can be used as valid Income proof for the person who are self employeed, as this is the only legal documents to verify income
Flawless proceesing of loan
Now a days every financial institution ask for ITR copy for loan processing as it works as valid income statement and relying on this one can easily grant loan
Visa Prossing
As this works as valid income proof, it helps embasy to know income and capability to ensure travelling expenses
Interest Benefit
One can claim housing loan interest paid as deduction from his income and reduce taxabililty.
Loss Compensasion
You can claim losses incurred in business or capital loss on sale of any asset against income in particular year and reduce tax liability
Claiming Refund
One can claim refund of taxes already paid only by filng ITR.
Carry forward of losses
If at any point of time, losses are incurred in business, then one can carry forward these losses and set off it against next years income till some predermined time frame. This will help in reducing tax liability.
Consequences of Non filing or late filing of ITR
- Penalty upto Rs. 5000/- will be levied for non filing of ITR within due date
- Carry forward of losses is not allowed in return is not filed within due date
- If you have taxable income and return is not filed department can levy penalty for concealment of income or not disclosing proper income.
- One will not get refund of excess tax paid if return not filed
- One will loose interest on refund if return not filed within due date
- For late filing of return one need to pay interest as well for delayed payment of taxes. It will increase tax burden.
Conclusion
Filing IT return of sole proprietor is need of time which will give sole proprietor ample of benefits to run business and maximize earning and save on taxation.